Intro
The New Technology File System (NTFS) is a file system developed and introduced by Microsoft in 1995, It was produced to overcome some limitations and offer new features.
- Hard-links
- Improved performance, reliability, and disk space utilization
- Security access control lists
- File system journaling
Here are some files related to the NTFS file system and what are they used for:
- $MFT Store MFT record
- $MFTMirr Contains a partial backup of MFT
- $LogFile Transaction logging file
- $Volume Contain volume information such as label, identifier, and version
- $AttrDef Attribute definition
- $Bitmap Contains the allocation status of all clusters
- $Boot Contain the boot record
- $BadClus Mark clusters as bad clusters
- $Secure Contain information about the security and access control information
So I will start to discuss what we can get out of analyzing NTFS Artifacts.
MFT
“Master File Table” can be the most interesting place to look for artifacts as it stores in it a record of the metadata of every file on the system including its size, time and date values, permissions, and sometimes the content of the file if it’s small enough.
The $MFT file can be found on the root of the volume, I will use FTKImager to show how to extract $MFT files as this may be a little tricky.
First We can export the $MFT file to our device.
But actually, when we try to list it in the directory, we can’t see it.
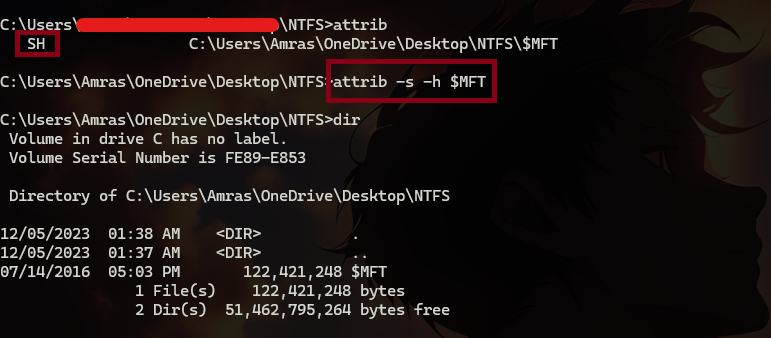
but if we used “attrib” command we can see that the $MFT file has two attributes “SH” which stands for system and hidden. so we can remove both of them then we can see it normally.
two main tools can be used to parse this file
- MFTexplorer
which views the content of the $MFT in an explorer view.
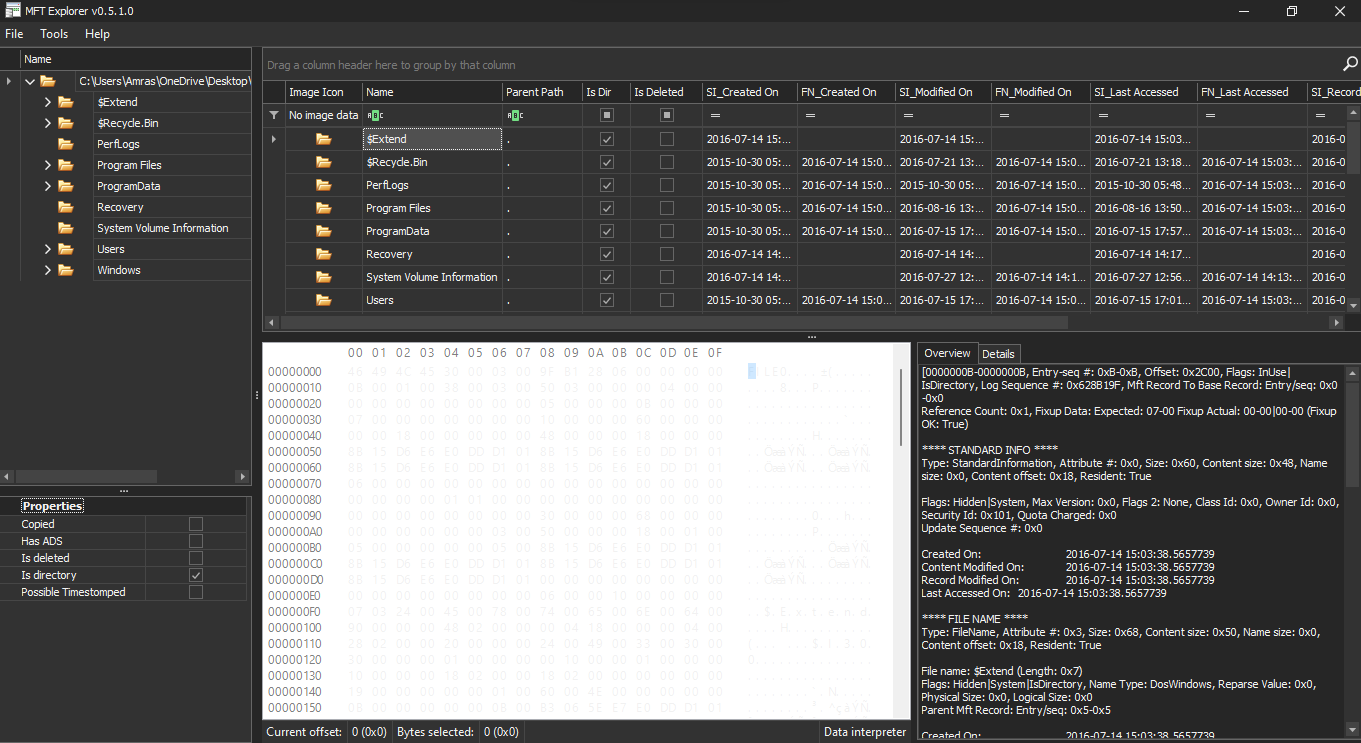
which is good for viewing the hierarchy of the volume content.
- MFTanalyzer
this one exports all the MFT content to a CSV file where you can do all the search and sort stuff.
python3 analyzeMFT.py -f MFT -o output.csv -eSo what we can do with that $MFT file?!
Actually, there is a lot that we can do, here are some examples:
-
knowing what files dropped to the disk at a range of time.
-
knowing when a specific file where last edited, deleted, or copied.
-
knowing if there is time stomping happened.
there is a lot to do, but I want to discuss the last one a little more “knowing if there is time stomping happened”.
time stomping is an anti-forensics technique in which the attacker randomly changes the dates of the creation modification and so on to prevent us from knowing the actual date and make it hard to sort and do this kind of stuff.
So let’s discuss MACB times in detail.
First “MACB” stands for:
- Modified
- Accessed
- Changed ($MFT Modified)
- Birth (file creation time)
and they are stored in $MFT under two attributes
- $STANDARD_INFO
- $FILE_NAME
what is really important to know here is that time Stomping tools can only mess with $STANDARD_INFO as $FILE_NAME is only writable by the kernel, so you can detect time stomping by comparing both of them.
here I will move to discuss how MACB time stamps work in NTFS.
MACB Time Stamps
let’s discuss what happens in the most happening scenarios:
File Download
All of the timestamps indicate a time of download, but there may be some exceptions as some browsers download content into a temp file and then rename it.
File Create
All of the time stamps indicate the time of creation.
file edit/modify
Changes only the Modify stamp.
file copy
Changes both the creation and the Accessed time stamps
Note: A great way to spot if a file was copied is to compare the creation time with the modification time.
If modification < creation then it's copied.file rename
Renaming a file will change modifications and change time stamps.
Journal
Journaling is a feature present in a lot of file systems, which is responsible for tracking changes that happen to the system and storing them to be able to roll back if needed.
NTFS has two journals
- USN Journal
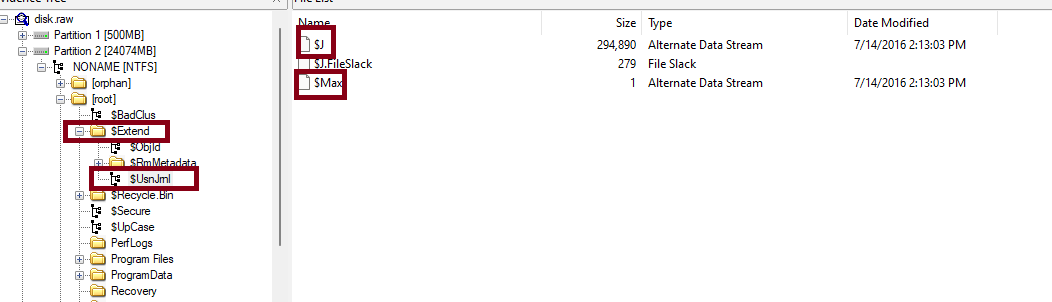
can be found in $Extend\$USNJRNL which consists of $Max which contains Additional data streams and $J which tracks changes alongside the reason for the change, this is the most important one for now.
- LOGFILE
can be found in the root of the volume $LogFile which keeps track of the changes for the $MFT metadata itself.
A nice tool to parse these artifacts is MFTECmd.
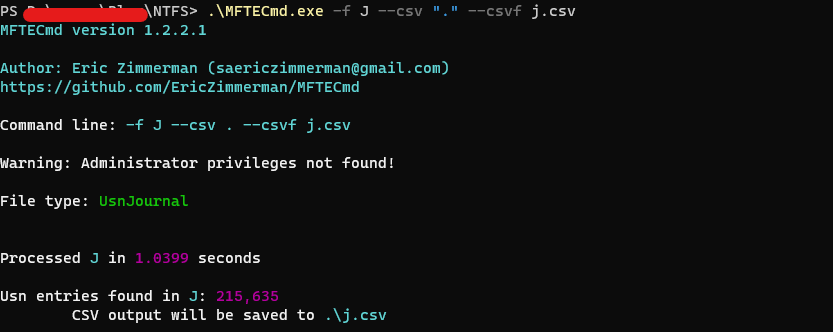
Demo
Now let’s do a demo testing what we talked about, to do that I created five test cases on my system to see what artifact these test cases left behind.
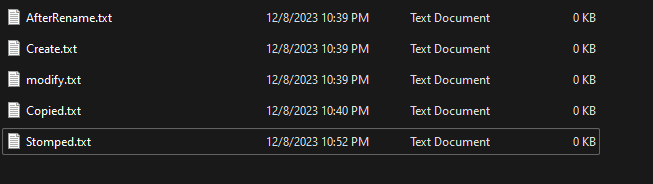
the test cases are:
- create file.
- Delete file.
- Rename file.
- Modify file.
- copy file.
- stomped file.
then I extracted the artifacts places that we mentioned before.
then I used MFTECmd to analyze them.
I started looking at $j file after parsing it using “MFTECmd”, and as we said journal tracks changes.
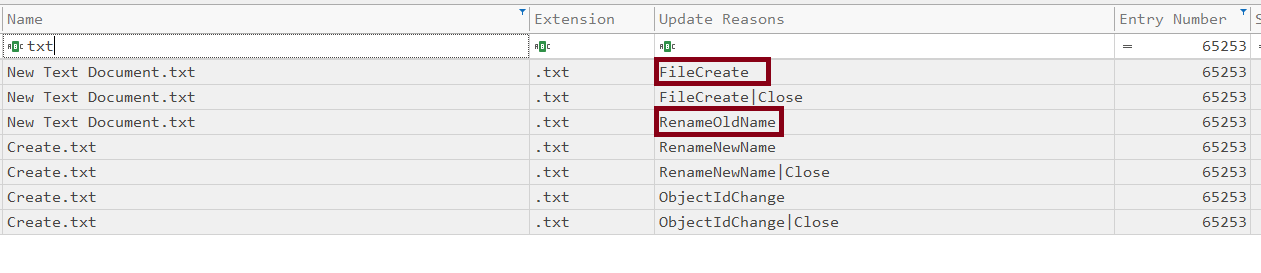
- Create:
when you create a file using gui by (right click -> new -> text file) you actually create a new text called “New Text Document.txt” Then you rename it so you can use it as evidence that the file was created using GUI.
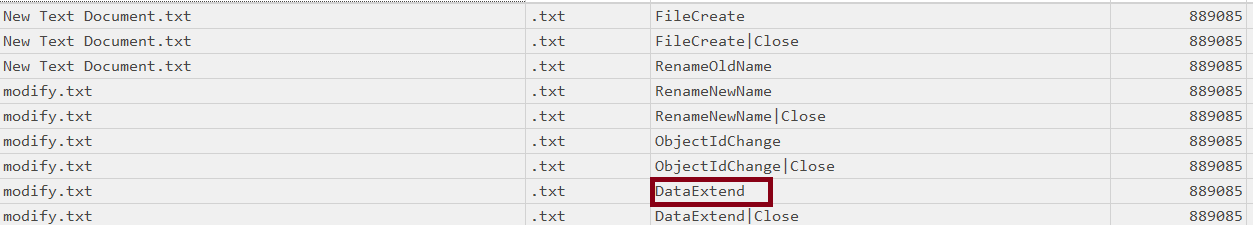
- Modify
for modification, we have a new entry “Data Extend”
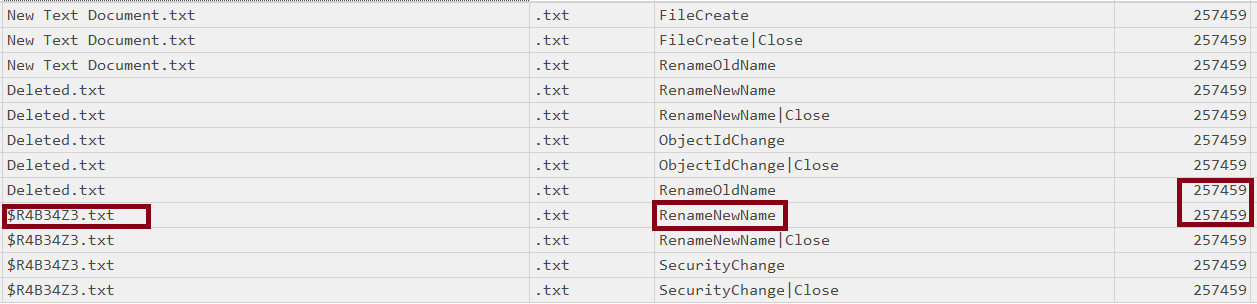
- Delete
what we can see in the delete case is that there is no action for deletion but instead, we will notice a rename for the file with the recycle bin schema “$R”
Now let’s move to MFT.
- Copy
We can see that the time stamp shows that the file was modified before creation which indicates a copy.

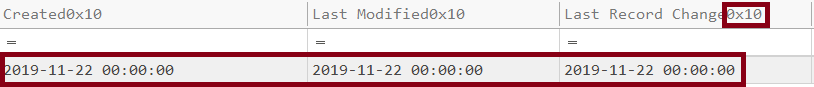
- Stomping
For the stomped file as we said we can compare $STANDARD_INFO and $FILE_NAME,
here is $STANDARD_INFO(0x10).
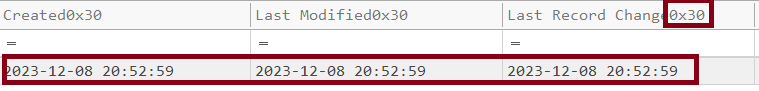
and the $FILE_NAME(0x30) which is only writable by the kernel.
Summary
In the end, NTFS is always the place where every disk-related artifact will leave a trace, Mastering its analysis is a crucial skill to have as this will make your investigation much more easier.
Author: Amr Ashraf